Virgil Tyler
6154
30783
59
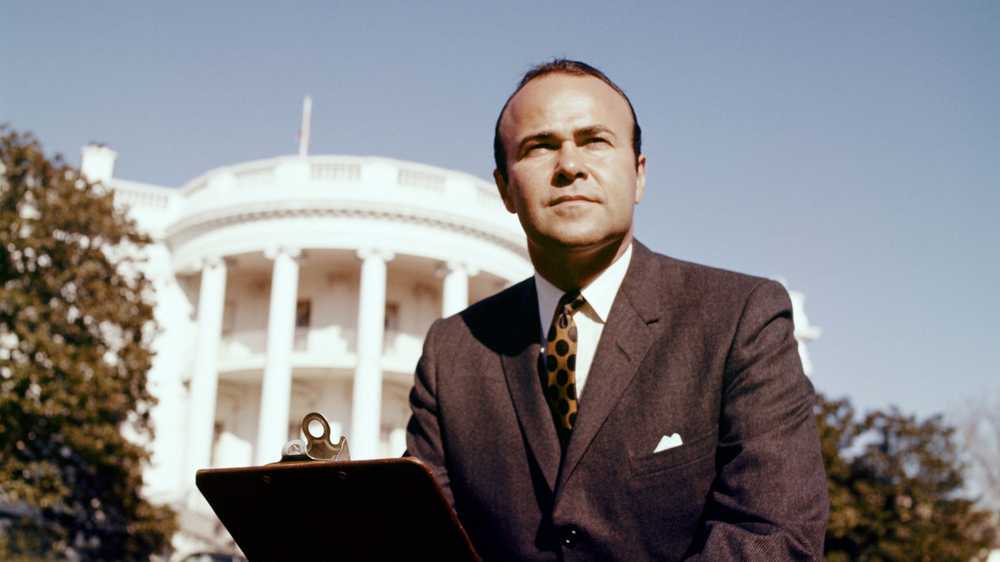
Dove si stava facendo la storia, Sander Vanocur era spesso lì con domande difficili. Il giornalista pionieristico che ha coperto la politica per la televisione e la stampa per più di 40 anni è morto di complicazioni dovute alla demenza lunedì 16 settembre 2019, mentre si trovava in ospedale a Santa Barbara, in California, secondo Il New York Times. Aveva 91 anni.
Vanocur è stato uno dei quattro giornalisti presenti nel panel del primo dibattito presidenziale televisivo tra Richard Nixon e John F. Kennedy, seguito da 70 milioni di telespettatori nel 1960. Più di tre decenni dopo, è stato uno dei relatori del dibattito tra George HW Bush, Bill Clinton e Ross Perot nel 1992.
Ha anche ospitato due serie sulla STORIA, Movies in Time e Storia & # x2019; s Business. Per Movies in Time, una volta ha intervistato Oliver Stone e Anthony Hopkins sul film del 1995 Nixon, confrontando le rappresentazioni del film con gli eventi storici reali. & # x201C; È & # x2019; s nell'occhio di chi guarda, & # x201D; Vanocur ha detto al Los Angeles Times della sua precisione. & # x201C; Una parte di me si ribella all'allentamento dei fatti. L'altra parte afferma che le persone hanno il diritto di interpretare la storia a modo loro ... Penso che stia mettendo in risalto le sue opinioni e le inserisca nel film, che è il suo diritto. Ma è una storia accurata? Non credo. # #2201D; penso di sì. & # X201D;
Lui stesso è apparso anche nei film come giornalista, con apparizioni nel 1971 La banda che non poteva sparare dritto, 1980 & # x2019; s Alza il Titanic, 1993 & # x2019; s Dave, 1996 & # x2019; s Scappare con l'omicidio e 1994 & # x2019; s Senza attenzione.Ha anche ricevuto il premio E. Van Scripps School of Journalism & # x2019; Carr Van Anda.
Nato l'8 gennaio 1928 a Cleveland, il suo nome era originariamente scritto Sander Vinocur. Ma dopo che sua madre e il padre avvocato divorziarono, si trasferì con i suoi figli a Peoria, nell'Illinois, e cambiò l'ortografia del loro cognome in Vanocur perché era arrabbiata con il vecchio, & # x201D; come Il New York Times dice Vanocur al giornale di San Pietroburgo, in Florida, The Evening Independent.
Vanocur si è laureato alla Western Military Academy di Alton, nell'Illinois e alla Northwestern University, e ha anche studiato alla London School of Economics. Ha anche prestato servizio nell'esercito.
Ha iniziato la sua carriera come reporter per The Manchester Guardian e ha lavorato per la BBC e la CBS News, prima di andare Il New York Times nel 1955. Nel 1957 si trasferì alla NBC News dove ricoprì diversi ruoli come corrispondente della Casa Bianca, Oggi mostra corrispondente D.C., Il Rapporto Huntley-Brinkley editore collaboratore e Primo martedì ospite. All'inizio degli anni '70 lasciò la NBC per la PBS, seguita da un periodo di lavoro Il Washington Post dal 1975 al 1977 e ABC News dal 1977 al 1991.
Tra le sue interviste più importanti c'erano la conversazione con Martin Luther King, Jr., presso la chiesa battista di Ebenezer meno di un anno prima che fosse assassinato e Robert Kennedy a Los Angeles presso l'Ambassador Hotel, poco prima che Kennedy fosse ucciso nel 1968.
& # x201C; Sono & # x2019; m un forte sostenitore della libertà di stampa & # x2014; purché abbiano qualcosa da dire, & # x201D; ha detto nel 2004 in un discorso alla Stanford University.
Vanocur era anche consulente presso il Center for the Study of Democratic Institutions, professore di comunicazione alla Duke University, residenza professionale presso il Freedom Forum di Arlington, in Virginia, e aveva una propria attività di consulenza in comunicazione, Old Owl Communications.
Era sposato con Edith Pick nel 1956 e aveva due figli, Christoper e Nicholas. Dopo la morte di Pick nel 1975, sposò Virginia Backus Vancour, che gli sopravvive. È sopravvissuto anche a una figliastra, Daphne Wood Hicks.
ALTRE STORIE DALLA BIOGRAFIA
 notizia
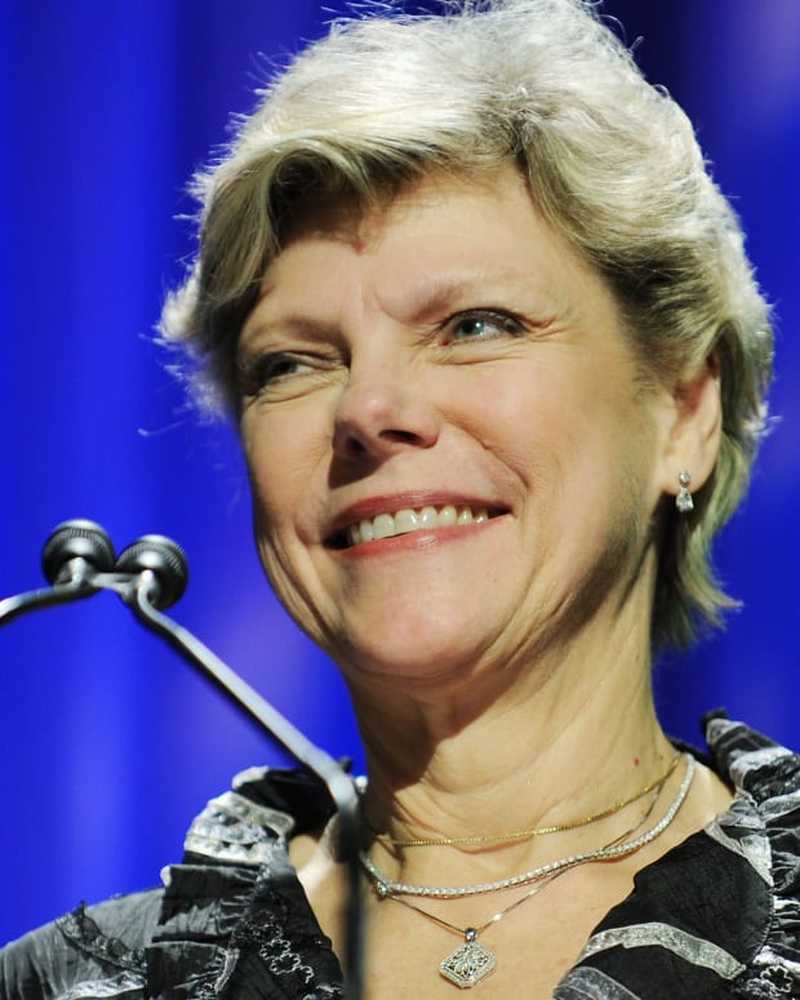
notiziaCokie Roberts, giornalista politico e autore di best seller, muore a 75 anni
Cokie Roberts, giornalista politico e autore di best seller, muore a 75 anni
- Di Rachel ChangSep 17, 2019
 Nelle news
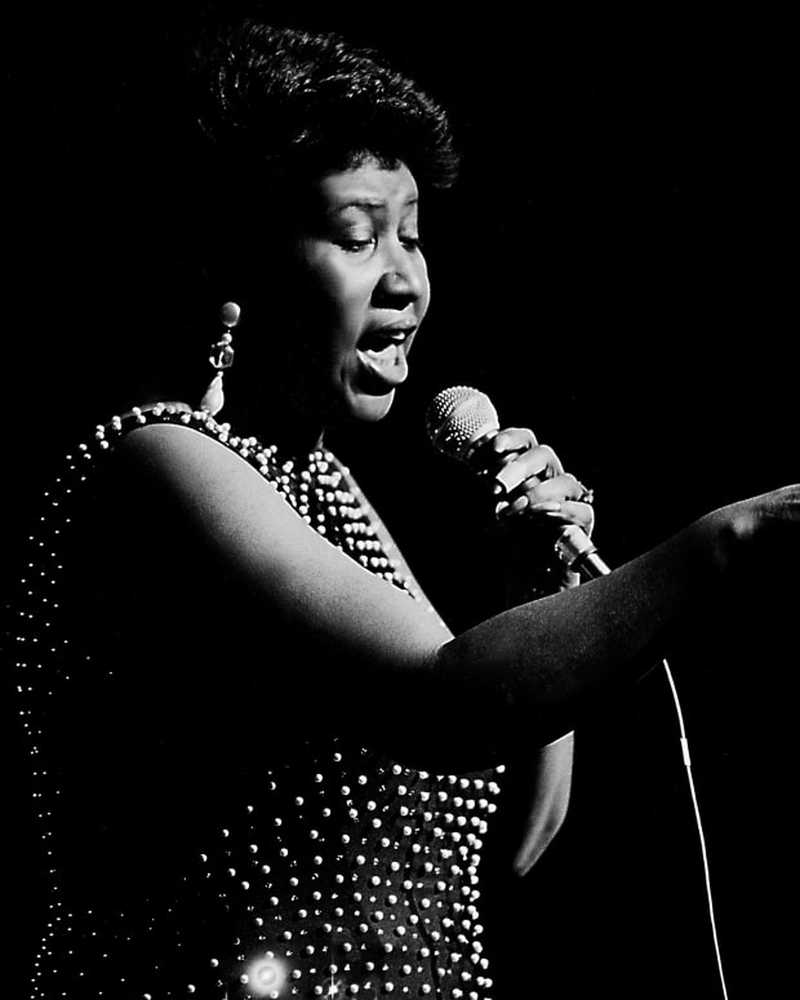
Nelle newsAretha Franklin muore all'età di 76 anni
La "Queen of Soul" lascia alle spalle un record di oltre 20 successi R&B in testa alla classifica e 18 vittorie di Grammy.
- Di David BlattyJun 16, 2019
 Nelle news
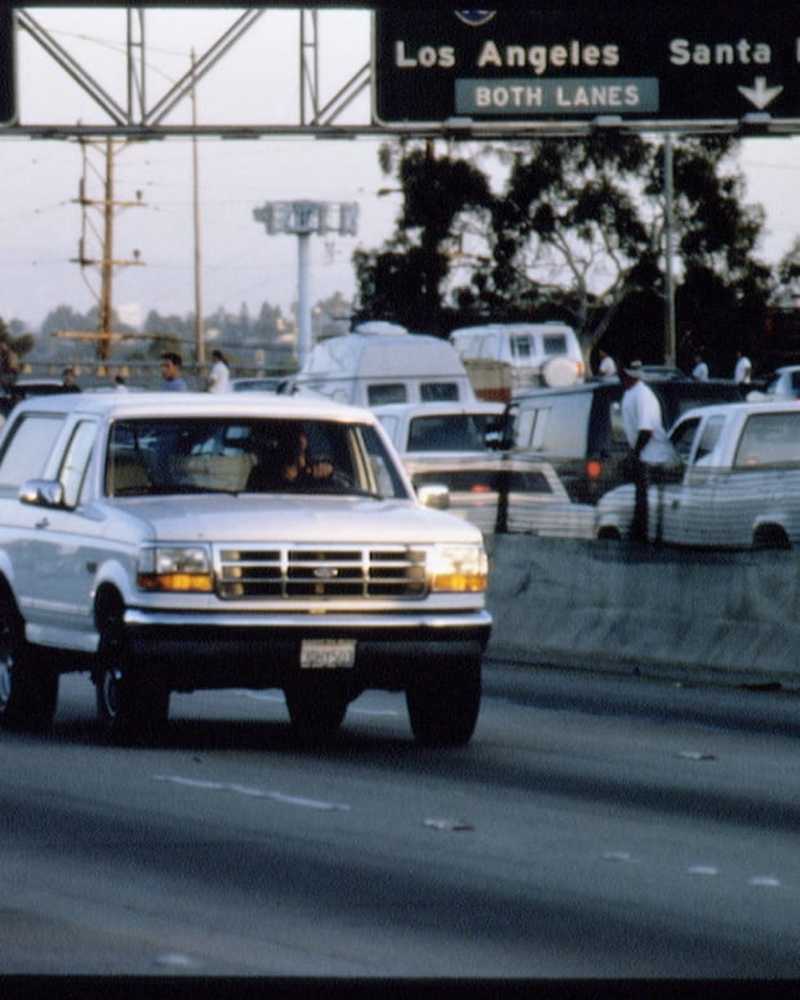
Nelle newsO.J. Simpson's Freeway Chase: What Happened to the White Ford Bronco
A più di due decenni dall'inseguimento a bassa velocità del sospetto omicida, la famigerata macchina si trova in un museo del crimine nel Tennessee.
- Di Rachel ChangJun 17, 2019
 Celebrità
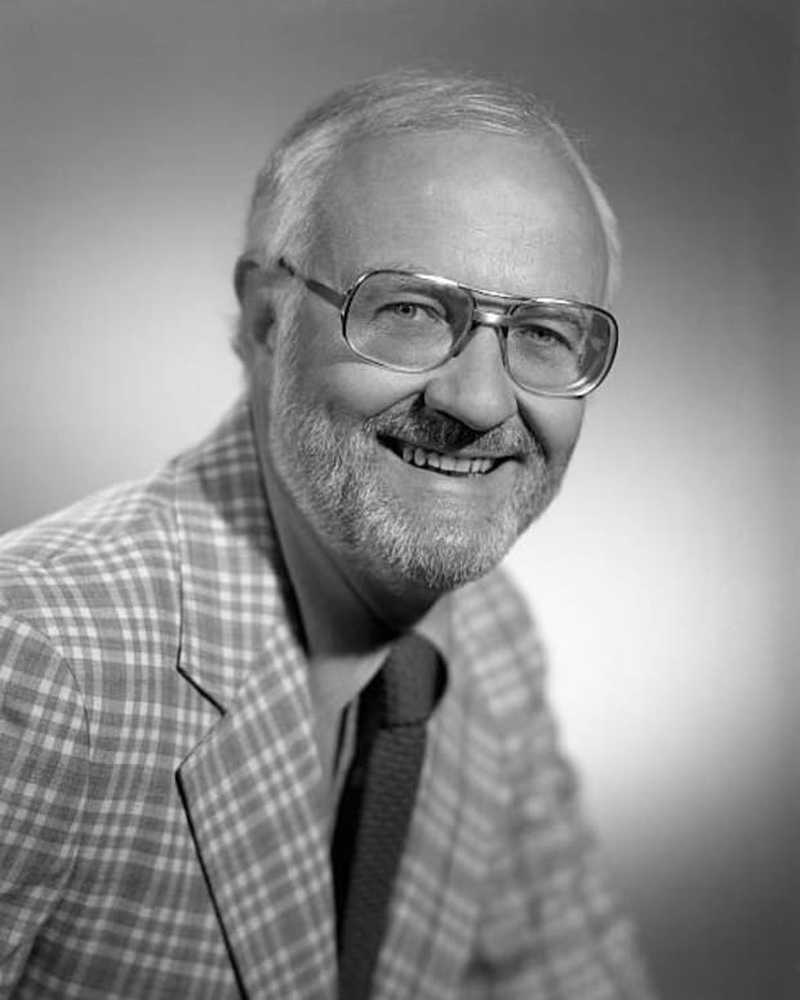
CelebritàJack Perkins, conduttore di "Biografia", muore a 85 anni
Il giornalista e commentatore ha ospitato la serie dal 1994 al 1999.
- Di Eudie PakAug 21, 2019
 Celebrità
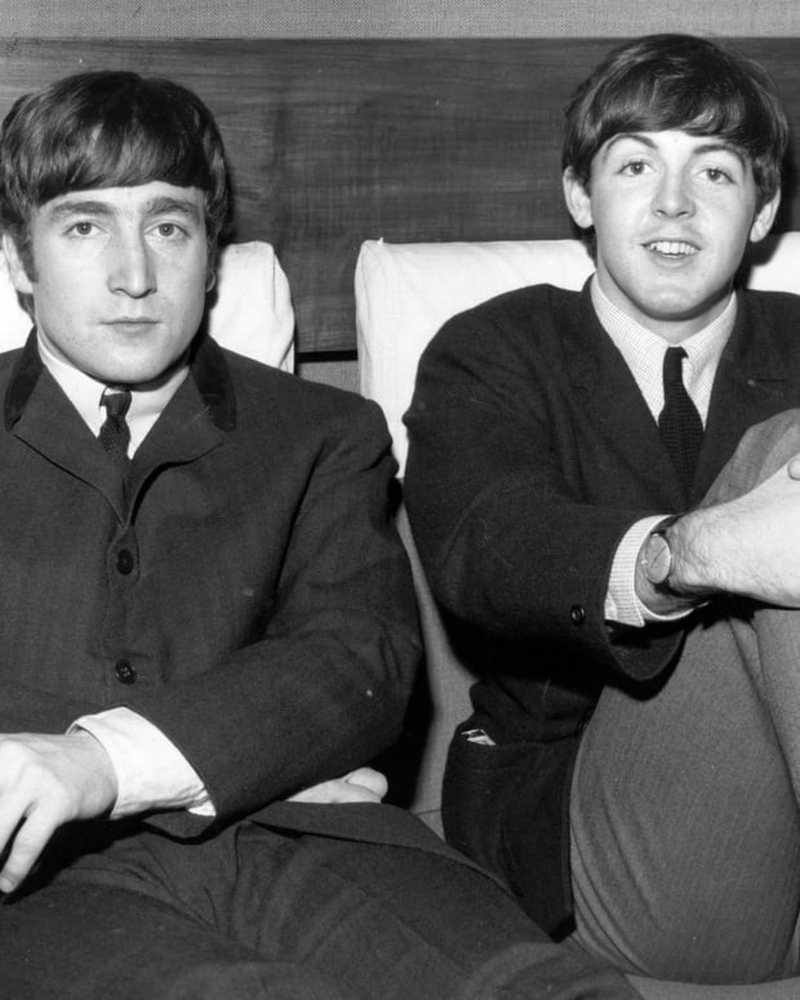
CelebritàAll'interno del legame 'Irreplaceable' di John Lennon e Paul McCartney - ed Epic Fall Out
Happenstance ha riunito una delle amicizie più vivaci nella storia della musica. Ma la tensione ha costretto i compagni di band dei Beatles a separarsi - fino a quando non hanno saputo che avrebbero dovuto lasciarlo.
- Di Rachel Chang, 24 settembre 2019
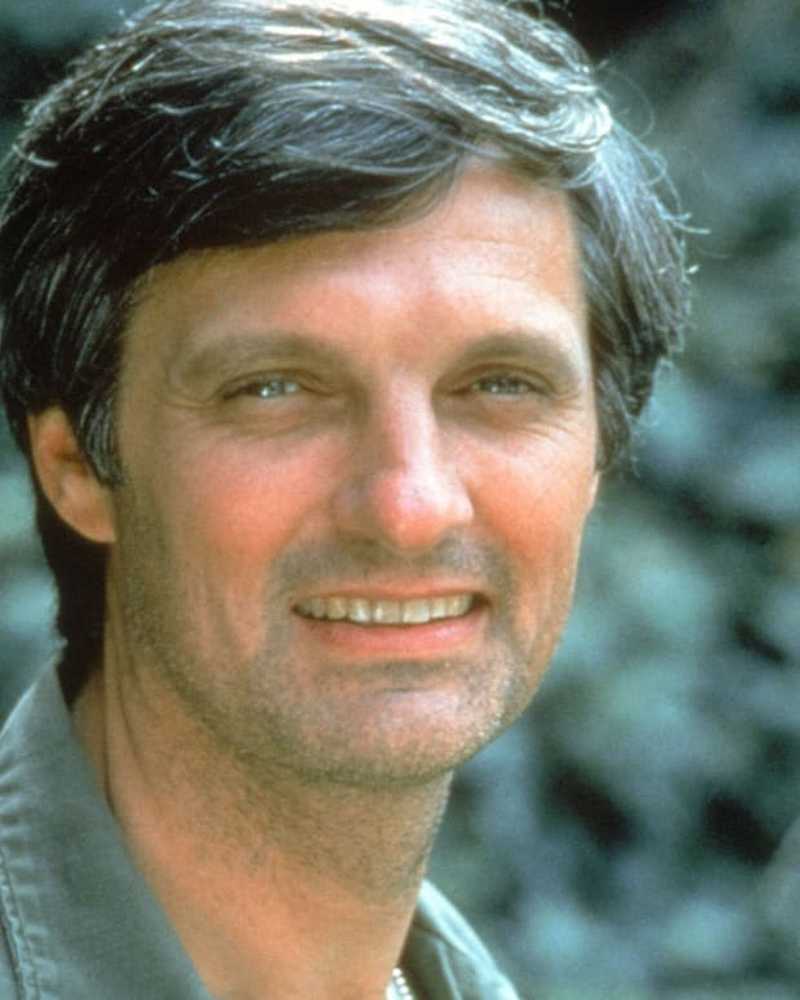 Nostalgia
NostalgiaStar TV che regnarono negli anni '70
Alan Alda compie oggi 80 anni. Per celebrare l'amato attore, stiamo dando uno sguardo al suo regno come un'iconica star televisiva degli anni '70 con i riflettori su alcune altre celebrità che hanno anche governato il decennio.
- Di Laurie UlsterJun 24, 2019
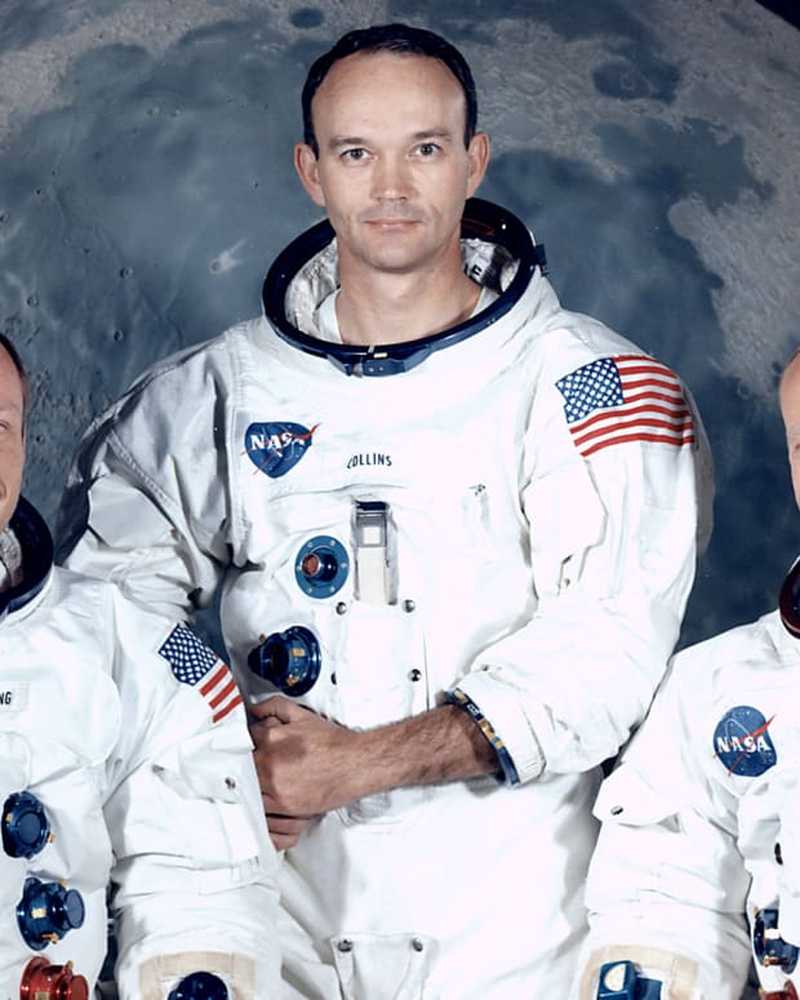 Storia e cultura
Storia e culturaCome Neil Armstrong e Buzz Aldrin sono stati selezionati per la missione Apollo 11
Ossessionati dal volo fin dall'infanzia, i veterani della guerra di Corea hanno unito le forze in una delle missioni spaziali di maggior successo di sempre, la passeggiata sulla luna del 1969.
- Di Rachel ChangJul 20, 2019
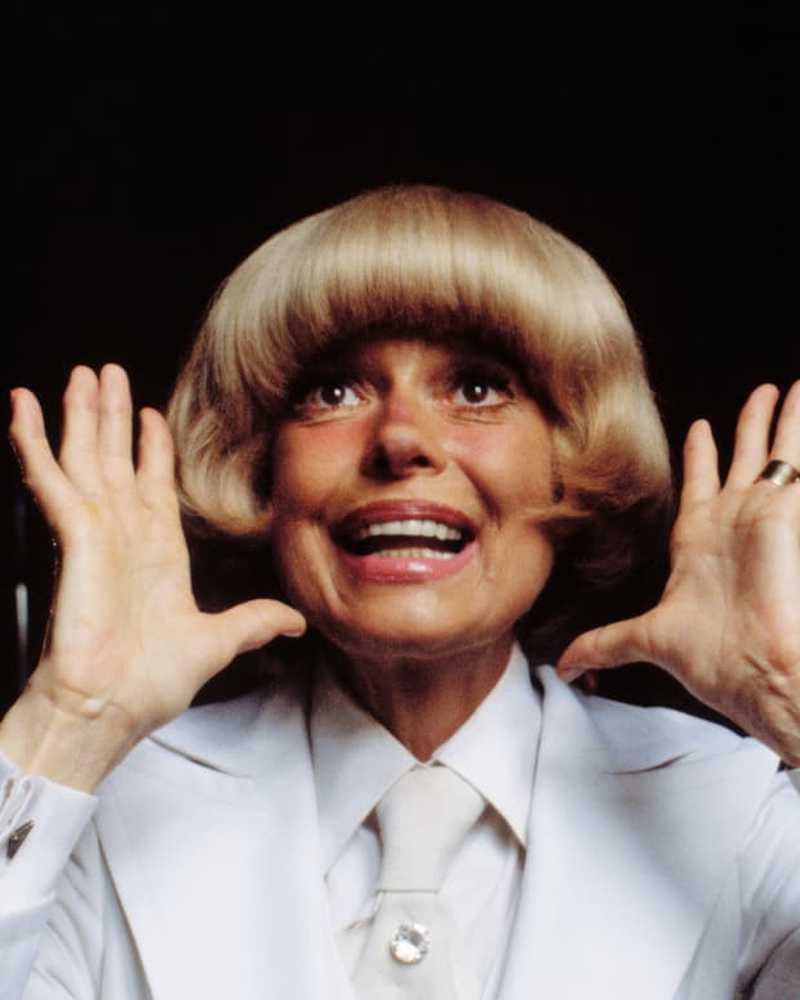 Nelle news
Nelle newsCarol Channing, l'amata Dolly di Broadway e Lorelei, muore a 97 anni
La performer è morta a casa sua in California.
- Di David ShewardJun 17, 2019
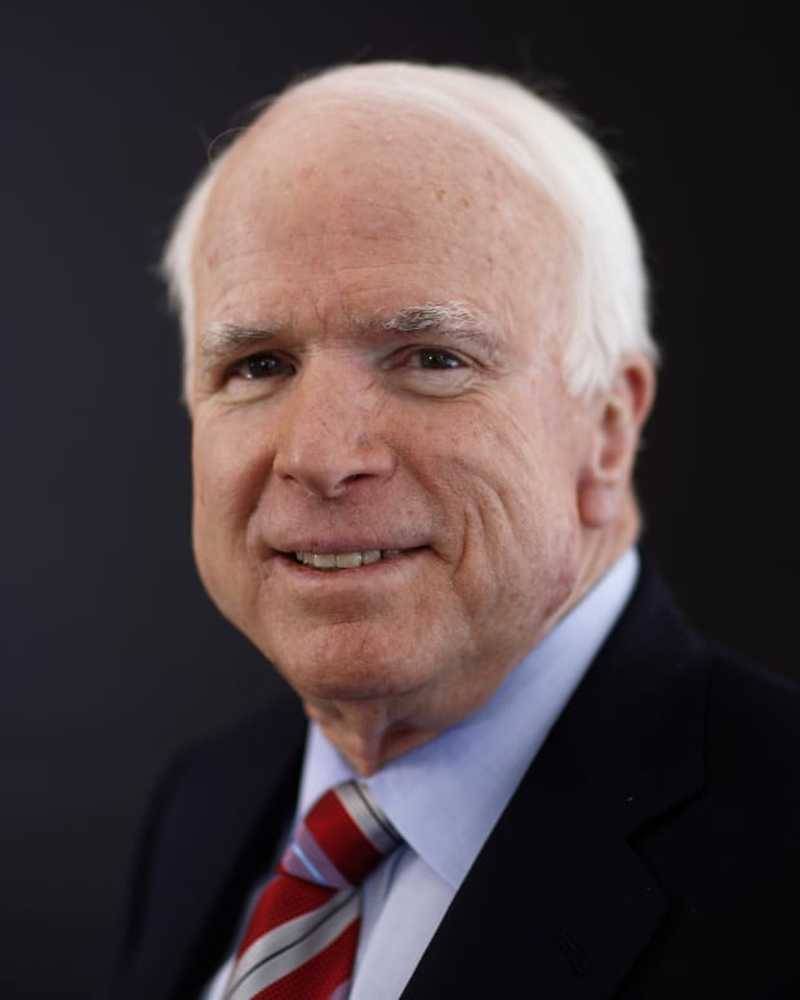 Nelle news
Nelle newsJohn McCain: War Hero, Senatore, Maverick è morto
Il senatore dell'Arizona sarà ricordato per molto tempo per essere rimasto fedele ai suoi principi e mettere il paese al di sopra della politica.
- Di Greg TimmonsJun 21, 2019